Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is a serious condition that can cause permanent damage to your hearing. Exposure to loud noises causes damage to the tiny hair cells in your inner ear. NIHL is preventable, but it cannot be reversed once it occurs. NIHL can greatly affect your quality of life, making communication and everyday tasks challenging.
This blog post will provide you with a comprehensive guide to NIHL. Discover its various types, recognize the symptoms, learn preventive measures, and explore treatment options. Additionally, we will explore the psychological impact of hearing loss and how hearing aids improve overall quality of life. Read on to learn more about noise-induced hearing loss and how to protect your hearing.
Table of Contents
What Are the 3 Main Types of Hearing Loss?
What Is Noise-Induced Hearing Loss?
What Is Noise-Induced Tinnitus?
What Is Occupational Hearing Loss?
How Common Is Ear Damage From Loud Noise?
Symptoms of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss Diagnosis and Treatment
How Does Hearing Loss Impact Mental Health?
What Level of Hearing Loss Requires a Hearing Aid?
What Are the Different Types of Hearing Aids?
What Are the Benefits of Hearing Aids?
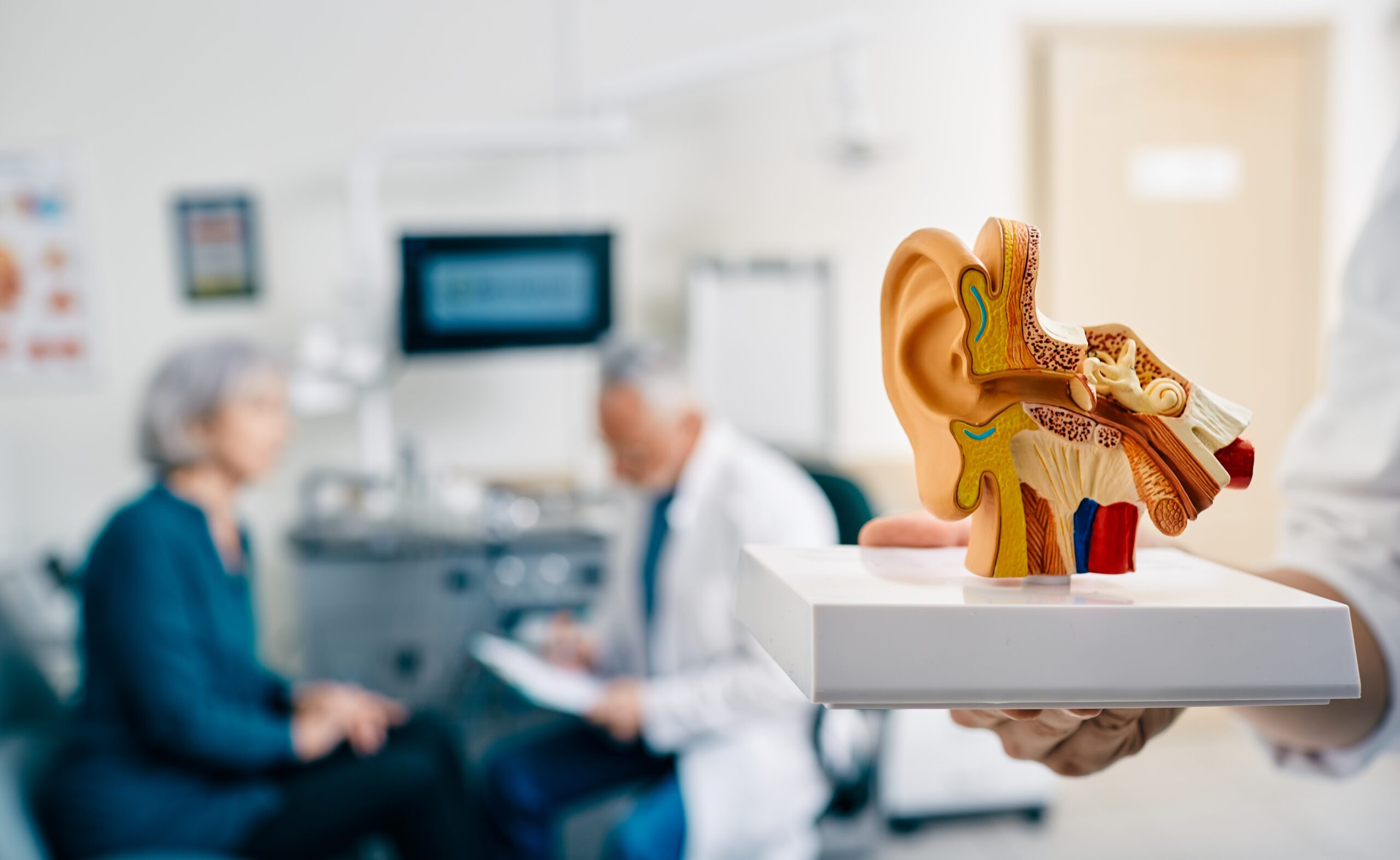
What Are the 3 Main Types of Hearing Loss?
Hearing loss can manifest in various forms, with distinct characteristics and underlying causes. Understanding these different types of hearing loss is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. The three primary categories of hearing loss are:
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common type. It occurs when there is damage to the delicate hair cells in the inner ear (cochlea) or to the auditory nerve. This damage can result from aging, exposure to loud noises, genetic factors, certain medications, or medical conditions. This type of hearing loss is permanent and typically leads to difficulty hearing faint sounds and understanding speech.
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss mainly results from outer or middle ear issues that disrupt sound transmission to the inner ear. Causes can include earwax blockage, fluid accumulation, ear infections, or structural abnormalities in the ear canal or middle ear. Medical or surgical interventions can often treat and resolve conductive hearing loss.</span
Mixed Hearing Loss
Mixed hearing loss is a combination of both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss. This means there is damage or impairment in both the inner ear or auditory nerve and the outer or middle ear. Mixed hearing loss can occur due to chronic ear infections, trauma, or a combination of genetic and age-related factors.
Because it involves elements of both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss, treatment options and outcomes can vary. It may include medical interventions like medication or surgery, as well as the use of hearing aids or other devices.

What Is Noise-Induced Hearing Loss?
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is a hearing impairment that occurs when the delicate structures within the inner ear sustain damage. Excessive exposure to loud sounds usually causes NIHL. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notes that this type of hearing loss cannot be medically or surgically corrected.
People in the agriculture, mining, construction, military, carpentry, and oil or gas extraction industries tend to suffer from NIHL. This is because work often exposes them to loud noises. However, NIHL can also result from exposure to loud noises in settings like concerts, sporting events, nightclubs, and more.

Causes of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
As the name suggests, exposure to excessively loud sounds is the primary cause of noise-induced hearing loss. These sounds can come from various sources and environments, including but not limited to:
- Occupational Noise. Construction workers, factory employees, and musicians face occupational noise daily. Prolonged exposure to these loud environments can lead to NIHL over time.
- Recreational Activities. Engaging in loud recreational activities like concerts, firearms, or motorcycles can put individuals at risk for NIHL.
- Personal Devices. The widespread use of personal audio devices, like headphones and earbuds, at high volumes can significantly contribute to NIHL. This is especially true among young people.
- Household Equipment. Frequent use of household appliances like lawnmowers, leaf blowers, power tools, and blenders can cause NIHL.

What Is Noise-Induced Tinnitus?
Noise-induced tinnitus is a specific type of tinnitus triggered by loud sounds. Tinnitus is the perception of sounds when there’s no actual external noise. With noise-induced tinnitus, loud sounds damage the sensitive inner ear hair cells and ear canal, causing sensations like ringing or buzzing in the ear. Sometimes, it goes away on its own, but often, it’s a chronic condition that can last for years or a lifetime.
Causes of Noise-Induced Tinnitus
The main cause is exposure to loud noise. This can result from one-time exposure to a loud sound or repeated exposure over time. Common sources of loud noise leading to tinnitus include:
- Construction sites
- Loud music
- Firearms
- Heavy machinery
- Industrial equipment

What Is Occupational Hearing Loss?
Occupational hearing loss occurs due to prolonged exposure to loud noise and ototoxic chemicals in the workplace. It’s a significant concern for those who work in noisy industrial environments, as it can have lasting and sometimes irreversible effects.
According to the CDC, noise is loud when it reaches 85 A-weighted decibels (dBA) or higher.
Causes of Occupational Hearing Loss
Several factors contribute to the development of occupational hearing loss, including:
- Exposure to Loud Noise. Prolonged exposure to loud noise, like in construction sites, factories, or manufacturing plants, can harm the delicate structures of the inner ear over time.
- Ototoxic Chemicals. Certain chemicals used in workplaces can have harmful effects on the auditory system. When absorbed or inhaled, these ototoxic chemicals can damage the hair cells in the inner ear and the auditory nerve.
- Traumatic Noise Events. Sudden, extremely loud noises, like explosions or heavy machinery accidents, can cause immediate and severe damage to the hearing organs.
- Age-Related Factors. Aging can compound the effects of noise and chemical exposure, making individuals more susceptible to occupational hearing loss.
- Cumulative Exposure. Aside from the noise or chemical exposure intensity, ongoing exposure over time can also lead to occupational hearing loss.
Symptoms of Occupational Hearing Loss
Recognizing the signs of occupational hearing loss is crucial for early intervention and prevention. Common symptoms include:
- Difficulty hearing in noisy environments
- Perception of mumbling or the need to ask for repetition
- Other people are noticing that you have difficulty hearing
- Tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ears)
- Ear pain or pressure
- Dizziness or balance problems
Promptly monitoring and addressing these symptoms is crucial to preventing hearing deterioration and maintaining well-being at work.
How Common Is Ear Damage From Loud Noises?
Ear damage from hazardous noise is more common than one might think, especially in today’s noisy environment. According to the WHO, 1.1 billion young people are at risk of permanent, avoidable hearing loss. This is mainly due to unsafe listening practices, such as using personal audio devices at high volumes or exposure to loud noises in recreational settings.
Symptoms of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) manifests through several key symptoms, including:
- Gradual hearing loss. NIHL typically causes high-frequency hearing loss, making it difficult to hear high-pitched sounds such as birds chirping. As NIHL advances, hearing loss can worsen and affect all frequencies.
- Tinnitus. Constant or intermittent tinnitus, a ringing or buzzing sound in the ears, is a common symptom of NIHL.
- Sensitivity to loud sounds. People with NIHL may be more sensitive to loud sounds due to damage in the inner ear, making it harder for the ear to process sound.
- Difficulty understanding speech. People with NIHL may struggle to understand speech in noisy environments due to background noise.
Recognizing these signs is essential, as prevention and early detection are crucial for preserving hearing health. Timely interventions can help reduce the long-term impact of NIHL and maintain your quality of life.

Hearing Loss Prevention Tips
You can identify and prevent NIHL before your hearing health is damaged. Here are some tips to help prevent NIHL:
- Protect your ears from loud noises. Wear earplugs, earmuffs, or other hearing protection when exposed to loud noise.
- Control volume levels. Keep your TV, radio, and other devices at a safe volume. Avoid high volumes when using headphones or earbuds.
- Avoid exposure to loud environments. Avoid loud places like concerts, nightclubs, and construction sites. If you find yourself in a noisy environment, use hearing protection.
- Perform regular hearing check-ups. Schedule regular hearing tests with your doctor or hearing healthcare professional to identify and treat hearing loss early on.
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss Diagnosis and Treatment
An audiologist can diagnose noise-induced hearing loss through a hearing evaluation. This evaluation will measure your ability to hear different pitches and volumes of sound. The audiologist will also ask about your history of exposure to loud noises.
NIHL is a permanent condition, but treatments are available to help manage the symptoms and improve communication. The most common treatment for NIHL is hearing aids. Hearing aids amplify sound so that you can hear better.

How Does Hearing Loss Impact Mental Health?
Hearing loss, whether mild, moderate, or severe, can significantly impact mental health. It can impair our ability to communicate and socialize and affect the quality of our relationships with others. Losing one’s ability to hear and understand sounds can make one feel isolated from the rest of the world.
What Are the Psychological Effects of Hearing Loss?
- Social isolation. Hearing loss can cause isolation as individuals may withdraw from social interactions due to communication challenges.
- Depression and anxiety. Struggling to hear and communicate can lead to depression and anxiety and impact mental well-being.
- Lower self-esteem. People with hearing loss may feel inadequate or burdensome, resulting in low self-esteem and insecurity.
- Reduced cognitive function. The effort to decipher speech in noisy environments can divert cognitive resources, potentially leading to cognitive fatigue.
- Communication challenges. Hearing loss can make it difficult to communicate with others, leading to frustration and misunderstanding.
Recognizing the psychological effects of hearing loss is essential. Addressing hearing loss and seeking intervention can improve mental well-being and overall quality of life for individuals with hearing impairments.
What Level of Hearing Loss Requires a Hearing Aid?
Levels of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is typically categorized into several levels based on the severity of the impairment. These levels help determine when a hearing aid is necessary to improve one’s auditory experience. The categories of hearing loss are the following:
- Mild: 25 to 40 dB.
- Moderate: 41 to 55 dB.
- Moderate-severe: 56 to 70 dB.
- Severe: 71 to 90 dB.
- Profound: when greater than 90 dB.
The decision of whether or not to use a hearing aid is a personal one. There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question. However, people with mild hearing loss may benefit from a hearing aid. Hearing aids may not provide noticeable benefits for individuals with profound hearing loss.
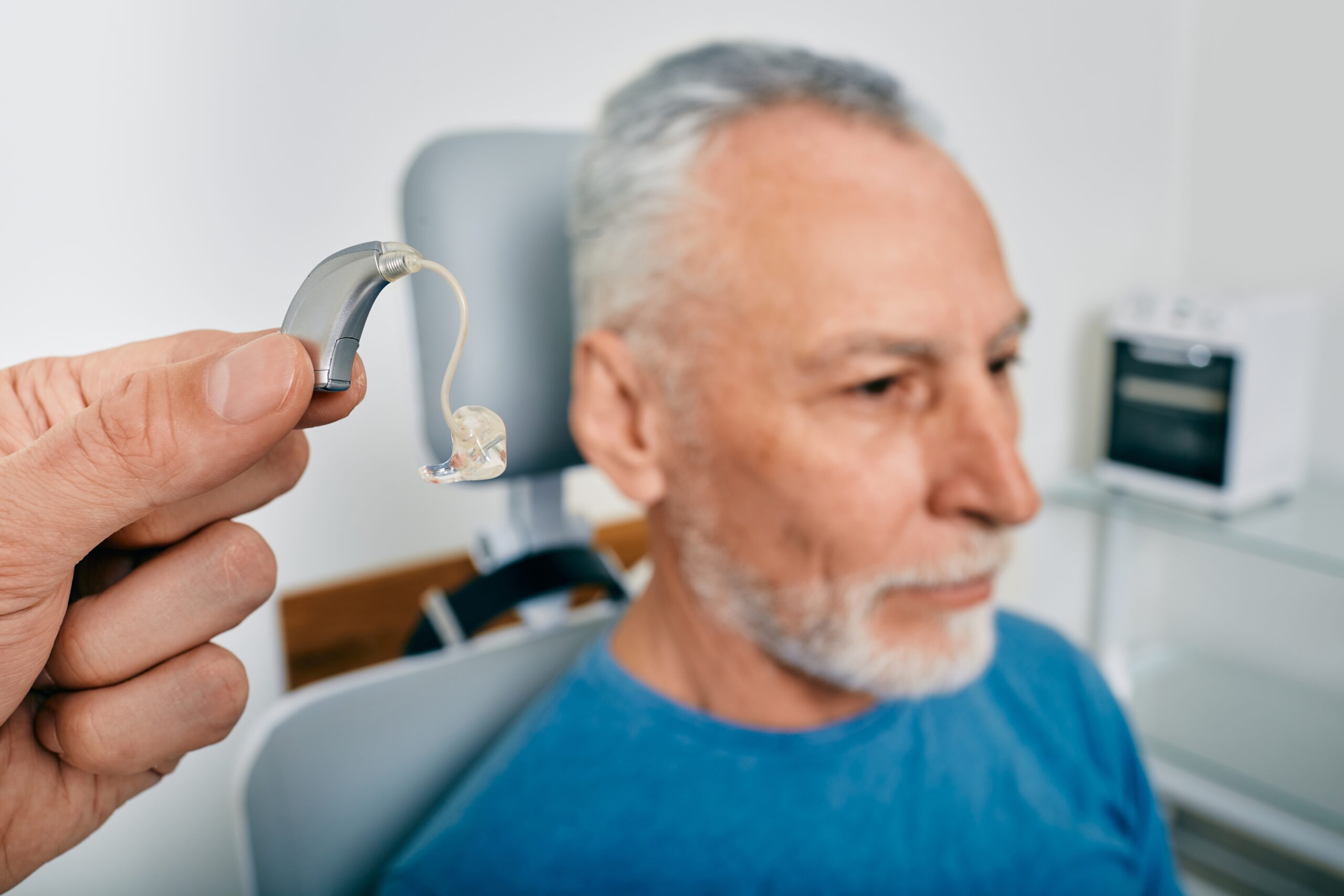
What Are the Different Types of Hearing Aids?
Hearing aids come in various styles and designs to cater to individuals with hearing loss’s diverse needs and preferences. These are the four main types of hearing aids:
Behind-the-Ear (BTE)
BTE hearing aids are the most common type of hearing aid. They are worn behind the ear and are available in various sizes and colors. BTE hearing aids are typically easy to use and maintain.
In-The-Ear (ITE)
ITE hearing aids are worn inside the ear and are less visible than BTE hearing aids. ITE hearing aids come in various sizes and styles based on your hearing loss severity and ear canal size.
Receiver-In-the-Ear (RITE)
RITE hearing aids are a type of BTE hearing aid that has a receiver that sits inside the ear canal. RITE hearing aids are less visible than traditional BTE hearing aids. They are often a good choice for people with mild to moderate hearing loss.
Custom Hearing Aids
Custom hearing aids are made to fit your ear canal specifically. They’re the most discreet hearing aids and often a good choice for mild to severe hearing loss.

What Are the Benefits of Hearing Aids?
Hearing aids are advanced devices that amplify sounds and improve your hearing. They capture sounds with a microphone, convert them to electrical signals, and deliver amplified sound to your ear. This process greatly enhances your hearing, making sounds clearer and easier to hear.
Purpose of Hearing Aids
Hearing aids serve a variety of purposes, including:
- Amplifying Sounds. The primary purpose of hearing aids is to make sounds louder and more audible for individuals with hearing loss.
- Improving Clarity. Hearing aids amplify sound and improve clarity, making it easier to understand speech and distinguish between different sounds.
- Reducing Listening Effort. Hearing aids reduce the effort required to hear, which can be particularly beneficial in noisy environments or during conversations.
- Restoring Confidence. Improved hearing can boost self-confidence, as individuals feel more engaged and capable in social and professional situations.
- Enhancing Safety. Hearing warning signals, alarms, and important environmental sounds enhances safety and awareness.
Benefits of Hearing Aids
In addition to their primary purposes, hearing aids can also offer several other benefits, including:
- Improved Communication. Hearing aids can improve communication with friends, family, and colleagues. This can lead to stronger relationships and a more fulfilling social life.
- Enhanced Quality of Life. Hearing aids improve your quality of life, making it easier to enjoy activities like music, TV, and socializing.
- Increased Independence. Hearing aids help maintain independence by facilitating everyday tasks like driving, shopping, and phone conversations.
- Better Cognitive Function. Addressing hearing loss with hearing aids can help maintain cognitive function and reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
- Improved Mental Health. Hearing aids can alleviate feelings of isolation, depression, and anxiety associated with untreated hearing loss.
- Increased Safety. Hearing aids can help to increase safety by making it easier to hear traffic, warning signals, and other important sounds.
Incorporating hearing aids into your daily life can provide many remarkable benefits. These devices are instrumental in helping individuals with hearing loss regain the ability to participate fully in the world around them.
Begin Your Journey to Better Hearing With Great Hearing Benefits
Hearing loss can have a significant impact on your quality of life. It can make communicating with friends and family difficult, participating in social activities, and even staying safe. If you are experiencing hearing loss, it is important to seek professional help.
Great Hearing Benefits is a leading provider of hearing aid discounts and comprehensive hearing care. We partner with health plans, employers, unions, and organizations to assist individuals with hearing loss access to top healthcare and technology. Contact Great Hearing Benefits today to learn more about our affordable hearing technology discounts and comprehensive hearing care solutions.



